Python is popular language due to its simple syntax and user friendly properties. It is used in almost every domain form web development to scientific research and development applications. In this article python has been used to develop a simple GUI which used to control some hardware using a micro-controller. Video below shows the working of that GUI.
Components Needed
- Arduino UNO
- LED
- Breadboard
- Jumper wires
- Power supply
- Laptop with python installed
Schematic and Circuit
User have to command the controller using GUI. Controller will accept the command and process it to give the out put. Schematic given below shows the process flow.
Figure given below shows the circuit diagram of this article. GUI is run on the computer screen and a serial communication connection between Arduino and Computer is established using USB. The command from GUI send to Arduino using this connection. A 5V DC power supply is used to power up the Arduino as well as LED. However it should be noted that, Arduino is connected to computer through USB so we do not need to supply the power to Arduino using some external source. If Arduino is not connected to computer then we need to power it up using some external source as shown in figure below.
GUI
The GUI is developed using Tkinter module in python language. Basically it contains three control buttons -
- ON
- OFF
- QUIT
 |
| Showing Status of LED in status bar when LED is ON. |
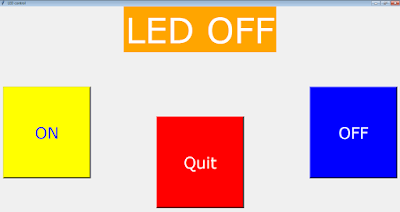 |
| Showing Status of LED in status bar when LED is OFF. |
Arduino Code
NOTE - You will see little difference in the GUI shown in video and GUI discussed here. GUI discussed here, is the improved version while GUI shown in video is the initial version.
Conclusion






Comments
Post a Comment