Created as a showcase project, AMAZE-28, the single-room summer house, was successfully constructed within 28 days on the grounds of the Kerala State Nirmithi Kendra. The 3D-printed building at the Kerala State Nirmithi Kendra in Thiruvananthapuram. (Photo: Shekunj) The inauguration of Kerala's inaugural 3D-printed structure, a 380-square-foot single-room summer house, is scheduled to take place on October 10 at the Kerala State Nirmithi Kendra (Kesnik) campus located in PTP Nagar, Thiruvananthapuram. Conceived as a showcase initiative, the summer house named AMAZE-28 was successfully finished within a mere 28 days. This impressive project was executed by Tvasta, a construction technology startup based in Chennai, founded by alumni of IIT-Madras, who have entered into a memorandum of understanding (MoU) with Kesnik. AMAZE-28 is perched upon a concrete foundation atop a gentle elevation within the Kesnik campus. Febi Varghese, the Director and Chief Executive Officer of...
This tutorial will guide you
through setting up MicroPython on NodeMCU, getting a prompt, using WebREPL,
connecting to the network and communicating with the Internet, using the
hardware peripherals, and controlling some external components.
Requirements –
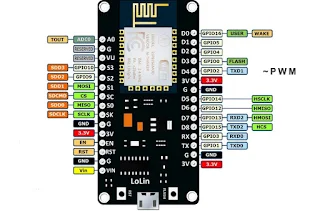
1. NodeMCU
Module
2. Laptop
with Python installed. (Here I am using python 2.7).
3. Internet
connection
Connecting the board to Power-
Connect the board to your laptop
through USB to power it up. You can also give it external power supply at Vin pin (shown in fig.
below). Please refer to the documentation for your board for further details.
Figure 1:
NodeMCU Module
Firmware download –
Download the most recent
MicroPython firmware .bin file to load onto your NodeMCU device. You can
download it from here,
and place it in your python/Scripts directory from earlier (screenshot).
Flashing the Firmware –
Before flashing the firmware I
assume that you have python (2.7) with pip tool.
So, follow the following steps –
·
cd /
·
cd Python27 (or whatever directory you installed
it to)
·
cd Scripts
·
pip install esptool
esptool – it is a Python-based, open source, platform independent,
utility to communicate with the ROM bootloader in Espressif ESP8266.
- Plug your USB cable into the NodeMCU board, and then into your computer.
- Go into device manager and confirm what port your device is on. We'll need this information later. I'm on COM port 3 (screenshot).
- Place the NodeMCU board into bootloader mode by holding the flash button, pressing the RST button, then releasing the flash button. You'll see the blue light briefly flash once when you've done this (screenshot).
- Open a command prompt, and return to the scripts directory.
- Run the following command, keeping in mind to substitute COM3 with YOUR particular COM port:
esptool.py
--port COM3 --baud 460800 write_flash --flash_size=detect 0
esp8266-20161110-v1.10.bin
Congratulations!!!!
You've successfully flashed Micropython onto a microcontroller!

Comments
Post a Comment